Skin cancers include melanoma, basal cell, and squamous cell. Basal and squamous cell are common and treatment is very effective. Malignant melanoma can be difficult to treat. 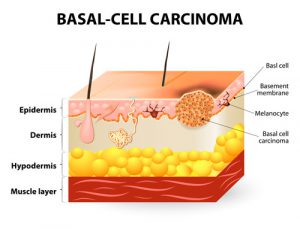 Early diagnosis and treatment can increase the survival rate from melanoma.
Early diagnosis and treatment can increase the survival rate from melanoma.
What Is Skin Cancer?
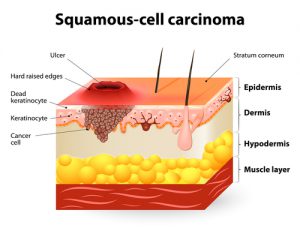
Skin cancers involve abnormal cell changes in the outer layer of skin. It is by far the most common cancer in the world, accounting for 75% of all cancer diagnoses. Most cases are cured, but the disease is a major health concern because it affects so many people. The incidence of skin cancer is rising, even though most cases could be prevented by limiting the skin’s exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Skin cancer is about three times more common in men than in women, and the risk increases with age. Most people diagnosed with skin cancer are between ages 45 and 54, although all forms of the disease are appearing more often in younger people. If you or any close relatives have had skin cancer, you are more likely to get the disease. Geography and race also factor into your chances of getting skin cancer, with the rate of skin cancer at its highest in places where fair-skinned Caucasians migrated from less sunny climates. Every malignant skin tumor in time becomes visible on the skin’s surface, making skin cancer the only type of cancer that is almost always detectable in its early, curable stages. Prompt detection and treatment of skin cancer is equivalent to cure.
Types of Skin Cancer Skin
Cancers fall into two major categories: melanoma and nonmelanoma. Melanoma can start in heavily pigmented tissue, such 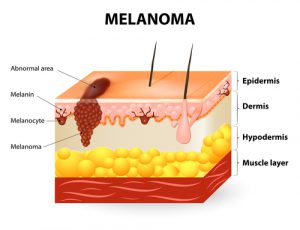 as a mole or birthmark, as well as in normally pigmented skin. Melanoma most commonly appears first on extremities, chest, or back, although it can occasionally arise on the palm of the hand; on the sole of the foot; under a fingernail or toenail; in the mucus linings of the mouth, vagina, or anus; and even in the eye. Melanoma is a potentially aggressive, life-threatening cancer. It is readily detectable and usually curable if treated early, but it progresses faster than other types of skin cancer and can spread beyond the skin to affect numerous parts of the body, including the bones or brain. Once this occurs, melanoma becomes very difficult to treat and is incurable.
as a mole or birthmark, as well as in normally pigmented skin. Melanoma most commonly appears first on extremities, chest, or back, although it can occasionally arise on the palm of the hand; on the sole of the foot; under a fingernail or toenail; in the mucus linings of the mouth, vagina, or anus; and even in the eye. Melanoma is a potentially aggressive, life-threatening cancer. It is readily detectable and usually curable if treated early, but it progresses faster than other types of skin cancer and can spread beyond the skin to affect numerous parts of the body, including the bones or brain. Once this occurs, melanoma becomes very difficult to treat and is incurable.
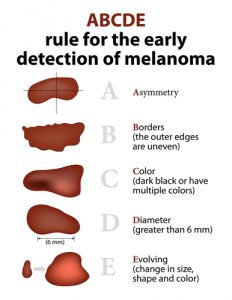 We posted an article about the A, B, C, D’s of detection. Click here to read.
We posted an article about the A, B, C, D’s of detection. Click here to read.





