Psoriasis (say “suh-RY-uh-sus”) is a long-term (chronic) skin problemthat causes skin cells to grow too quickly, resulting in thick, white, silvery, or red patches of skin.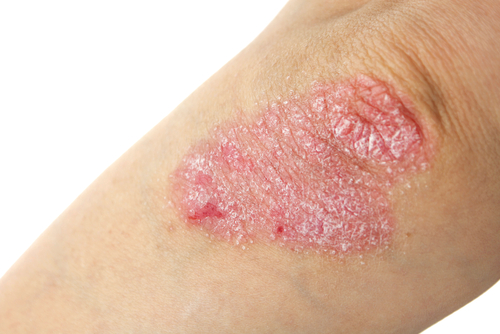
Normally, skin cells grow gradually and flake off about every 4 weeks. New skin cells grow to replace the outer layers of the skin as they shed. But in psoriasis, new skin cells move rapidly to the surface of the skin in days rather than weeks. They build up and form thick patches called plaques (say “plax”). The patches range in size from small to large. They most often appear on the knees, elbows, scalp, hands, feet, or lower back.
Psoriasis is most common in adults. But children and teens can get it too. Having psoriasis can be embarrassing, and many people, especially teens, avoid swimming and other situations where patches can show. But there are many types of treatment that can help keep psoriasis under control.
Experts believe that psoriasis occurs when the immune system overreacts, causing inflammation and flaking of skin. In some cases, psoriasis runs in families. People with psoriasis often notice times when their skin gets worse. Things that can cause these flare-ups include a cold and dry climate, infections, stress, dry skin, and taking certain medicines. Psoriasis isn’t contagious. It can’t be spread by touch from person to person. Symptoms of psoriasis appear in different ways. Psoriasis can be mild, with small areas of rash. When psoriasis is moderate or severe, the skin gets inflamed with raised red areas topped with loose, silvery, scaling skin. If psoriasis is severe, the skin becomes itchy and tender. And sometimes large patches form and may be uncomfortable. The patches can join together and cover large areas of skin, such as the entire back.
Psoriasis can also affect the fingernails and toenails, causing the nails to pit, change color, and separate from the nail bed.





